Infection or Injection? Associating Myocarditis and Pericarditis with COVID-19

Background Epidemiology of Myocarditis and Pericarditis
Myocarditis is defined as inflammation of the heart muscle not resulting from an ischaemic event (heart attack). It can manifest as sudden death, chest pain or heart failure presenting with exercise intolerance, breathing difficulties, fatigue and ankle swelling. Myocarditis is estimated to have been responsible for around 36.5 of every 100,000 hospital admissions in the UK between 1998 and 2017, but is likely under-diagnosed.
Pericarditis is defined as inflammation of the fine, double-layered sac which lines the heart muscle. The incidence rate is estimated at around 1 diagnosis for every 1,000 hospital admissions. Clinical presentation can be similar to myocarditis, but it is also thought to be under-diagnosed.
Myocarditis and pericarditis have a range of causes, including both systemic COVID-19 infection and administration of COVID-19 “vaccines”. The inflammation is thought to result from an auto-immune reaction to the presence of spike protein from either infection and/or vaccination, and lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) used in mRNA products (Pfizer and Moderna).
Investigating COVID-19 Associations With Myocarditis and Pericarditis
Government agencies and mainstream media have promoted theories that the increases in heart conditions being seen globally are a result of acute COVID-19 infection and/or Long Covid. These theories deserve close scrutiny given the background of ongoing mass administration of substances containing potentially inflammatory ingredients with the capacity to cause heart damage.
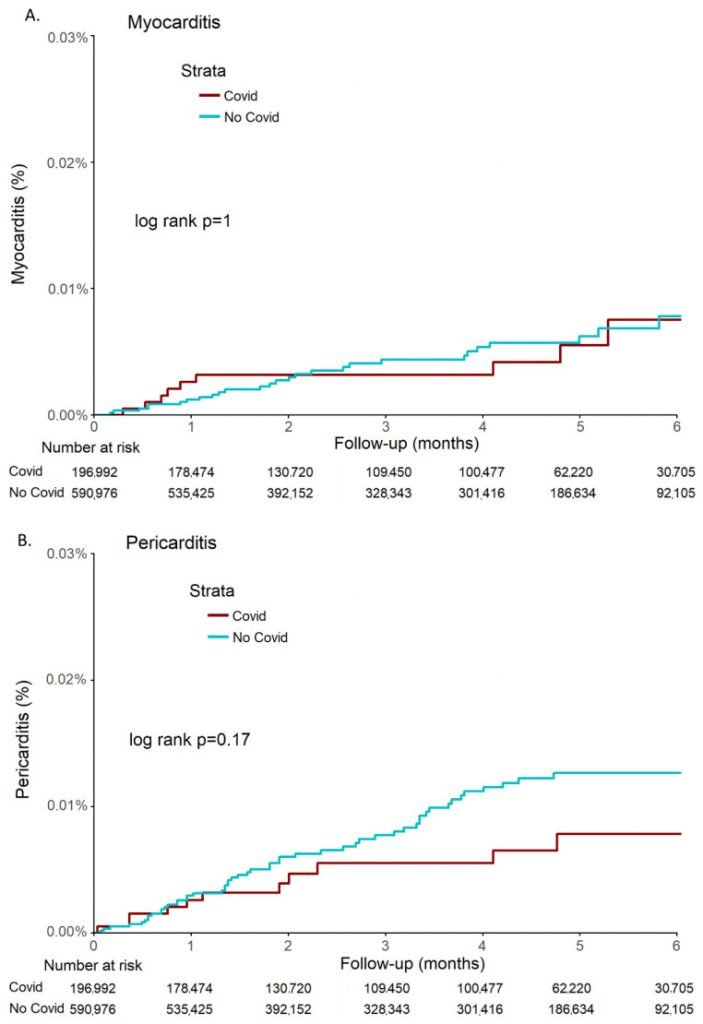
Published in the Journal of Clinical Medicine in April 2022, The Incidence of Myocarditis and Pericarditis in Post COVID-19 Unvaccinated Patients-A Large Population-Based Study is a retrospective cohort study of almost 200,000 Israeli adults diagnosed with COVID-19 prior to the vaccine rollout. NZDSOS drew attention to this study two weeks ago in a more detailed analysis of our public health concerns relating to the mass administration of the COVID-19 products referred to as “vaccines”. With the current media attention being given to heart disease and other worrying health outcomes in otherwise young and/or healthy people, we feel it is worth highlighting again.
The study findings support previous data showing that post-vaccine risk of myocarditis exceeds post-infection risk of myocarditis. They demonstrated no increased incidence of either condition in this large unvaccinated cohort over six months post-infection.
Another peer-reviewed study, Age and sex-specific risks of myocarditis and pericarditis following Covid-19 messenger RNA vaccines, was published in Nature on 25 June 2022. Across the total population aged 15 to 50 years in France, all cases of myocarditis and pericarditis diagnosed between May 2021 and October 2021 were compared against undiagnosed control groups. The groups were matched for age, sex and deprivation index rating (to reduce possible bias of socio-economic influences for ill health).
In comparing cases against controls, a higher proportion of cases had prior histories of myocarditis or pericarditis (the strongest correlation), of Covid diagnosis, or of having received an mRNA vaccine. The second strongest correlation was receiving dose 2 of an mRNA vaccine within seven days of symptom onset, most pronounced following mRNA-1273 (Moderna) which contains a larger dose of mRNA (100mcg compared with 30mcg in Pfizer). Causality is further discussed in our recent article Vaccine Injuries Part 6.
A common assertion is that Novavax, because it uses a more traditional vaccine technology, is safer than the mRNA substances. Yet in early June there were reports that FDA Flags Heart Inflammation Risk Over Novavax COVID-19 Vaccine, likely also relating to use of the spike protein as the target antigen. In addition to this, there are other safety concerns being reported, detailed in FDA Authorizes ‘Traditional’ Novavax COVID Vaccine, But Critics Question Safety Claims.
There have been claims, including by NZ government officials, that myocarditis related to the vaccines is “mild”. This is a medical untruth, contradicted by eminent physicians such as pathologist Dr Roger Hodkinson, vaccinologist Dr Robert Malone, cardiologist Dr Peter McCullough, and pathologist Dr Ryan Cole. The increase in sudden death being seen across the globe, likely as a result of heart damage in a significant proportion of these victims, described here by lung and ICU specialist Dr Pierre Kory of Frontline Covid-19 Critical Care Alliance (FLCCC), supports our concurrence with these medical specialists. Other physicians, we believe in increasing numbers, are expressing similar concerns, for example here and here.
Conclusion : Infection vs Injection
The causative agents for COVID-19-related myocarditis and pericarditis appear to be spike protein and lipid nanoparticles, when they reach the circulation and travel to the heart. For most people a COVID-19 infection stays in the respiratory tract where mucosal defense mechanisms usually block it from entering the circulation. An excellent review of this science is available at The Politicization of Immunology, by Associate Professor of Microbiology and Immunology, Steve Templeton.
The different COVID-19 vaccines all use different methods to introduce the spike protein directly into the circulation via injection. The presence of this protein then theoretically invokes an antibody response in order to provide protection against future infection. There are multiple flaws in this process, including but not limited to:
- rapidly waning post-vaccination antibodies compared to post-infection immunity, discussed here;
- rapid mutations on the spike protein (ie constantly evolving new variants) of the virus, such that current vaccines no longer match current circulating variants, discussed in detail here;
- the issue of immunobridging. This refers to measuring markers (such as antibodies circulating in the blood) which may not translate to actual protection against disease if other immune markers such as T-cells and complex processes in the respiratory tract are better indicators, but are not so easily measured. Further information on immuno-bridging is available at point #5, here;
- the risk of vaccine associated enhanced disease (VAED), discussed briefly here in relation to Novavax, and we have discussed VAED multiple times, most recently here; also here and here.
For those who are infected and at risk of, or who experience, serious illness, COVID-19 is a very treatable disease. Being aware of personal risk factors for serious illness (older age and obesity are the two most significant, but presence of chronic diseases such as diabetes and renal disease can also increase risk), and seeking appropriate medical attention when symptoms appear, are important protective measures. Optimising immune health via weight control, nutritious diet, appropriate supplementation, exercise, maintaining vitamin D levels are also imperative. Excellent protocols for prevention and treatment are available at the Frontline Covid-19 Critical Care Alliance (FLCCC).
In contrast to natural infection, vaccination introduces lipid nanoparticles (in the case of mRNA substances) and spike protein (in the case of all COVID-19 vaccines in current use) directly into the circulation. It was initially claimed that these ingredients stayed near the injection site where the local lymphatic system would induce an immune response. It has since been shown that the vaccine substances enter the circulation and travel throughout the body. In cases where they concentrate in or around the heart muscle, there is increased risk of an inflammatory response leading to myocarditis and/or pericarditis.
If you or someone you know has experienced an adverse event following COVID-19 vaccination, it is important to seek medical attention. It is also important to:
- report to Medsafe via an online CARM form;
- make an ACC claim;
- report to The Health Forum NZ who can add your details to the Citizens’ Database and offer support with ACC and CARM reporting if required.
If you are unable to find appropriate medical support, register with NZDSOS Help Clinic.





One Comment
Comments are closed.